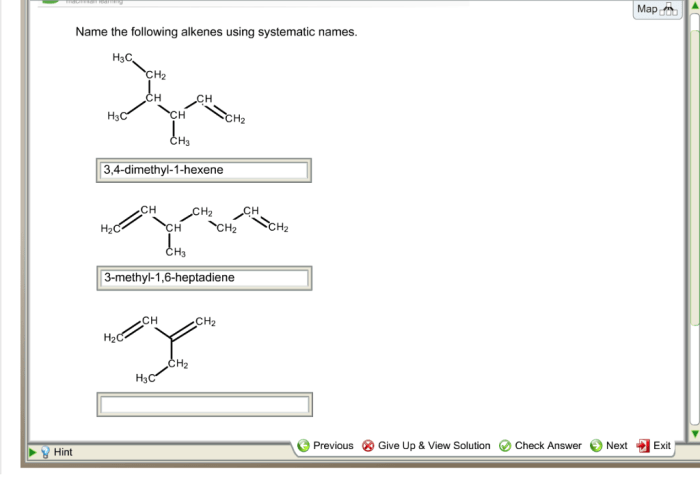
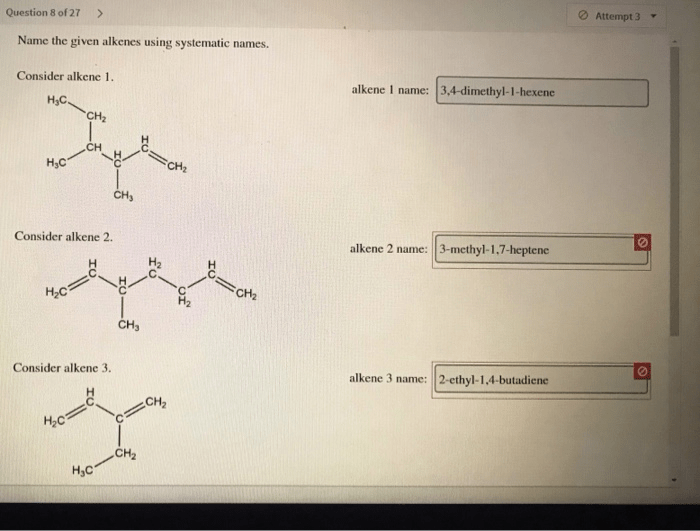
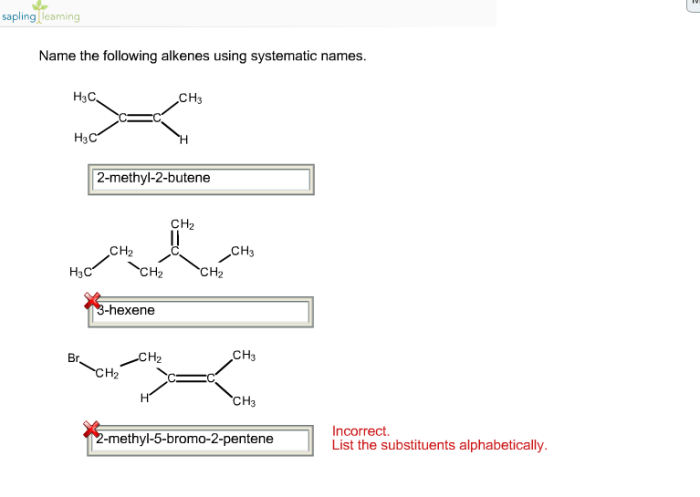
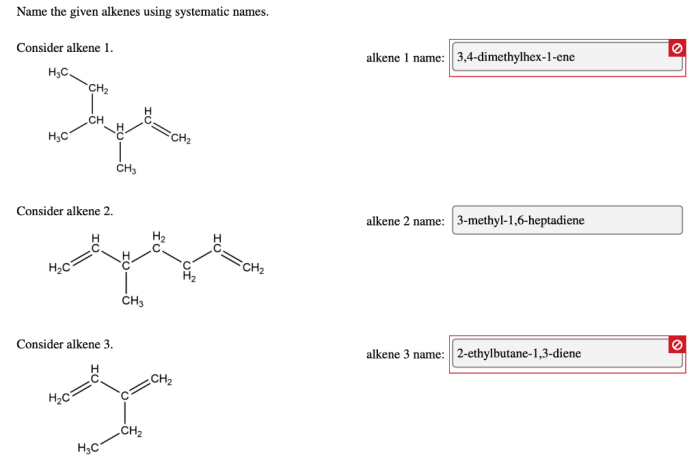
Name the given alkenes using systematic names. – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, we embark on a journey to unravel the systematic nomenclature of alkenes. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and understanding to decipher the intricacies of alkene naming, providing a solid foundation for further exploration in this fascinating field.
Alkenes, characterized by their unsaturated carbon-carbon double bonds, exhibit unique properties and reactivity that distinguish them from other hydrocarbons. By understanding the IUPAC guidelines for alkene nomenclature, we gain the ability to systematically assign names to these compounds, enabling clear and precise communication within the scientific community.
Systematic Nomenclature of Alkenes
In the IUPAC system, alkenes are named according to the following rules:
- The root name of the alkene is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
- The suffix “-ene” is added to the root name to indicate that the compound is an alkene.
- The location of the double bond is indicated by a number placed before the suffix. The number refers to the carbon atom at which the double bond begins.
- If there are multiple double bonds in the molecule, the suffix “-diene”, “-triene”, etc. is used.
- If there are other functional groups present in the molecule, they are named as prefixes.
For example, the systematic name for the alkene with the formula CH 3CH=CHCH 2CH 3is 2-pentene.
Identifying Alkenes
Alkenes can be distinguished from other hydrocarbons by their structural features.
- Alkenes contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
- The double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond.
- The carbon atoms in the double bond are sp 2hybridized.
- Alkenes are generally more reactive than alkanes.
There are several methods for identifying alkenes in a given compound.
- Bromine test:Alkenes react with bromine to form a dibromoalkane. This reaction can be used to distinguish alkenes from alkanes.
- Potassium permanganate test:Alkenes react with potassium permanganate to form a diol. This reaction can be used to distinguish alkenes from alkanes and alkynes.
- Spectroscopy:Alkenes can be identified by their characteristic infrared and NMR spectra.
Isomerism in Alkenes
Isomerism is the phenomenon of compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures.
There are two types of isomerism in alkenes:
- Structural isomerism:Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different bonding arrangements.
- Stereoisomerism:Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula and bonding arrangements but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
For example, butene has two structural isomers: 1-butene and 2-butene. Butene also has two stereoisomers: cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene.
Physical Properties of Alkenes
The physical properties of alkenes depend on their molecular weight and structure.
- Alkenes are generally nonpolar compounds.
- Alkenes are less dense than water.
- Alkenes are insoluble in water.
- Alkenes have lower boiling points than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms.
- Alkenes have higher melting points than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms.
Chemical Reactivity of Alkenes: Name The Given Alkenes Using Systematic Names.
Alkenes are highly reactive compounds.
Alkenes undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Addition reactions:Alkenes react with a variety of reagents to add atoms or groups of atoms to the double bond.
- Substitution reactions:Alkenes react with certain reagents to replace one of the hydrogen atoms on the double bond with another atom or group of atoms.
- Polymerization reactions:Alkenes can react with themselves to form polymers.
The reactivity of alkenes is due to the presence of the double bond.
Applications of Alkenes
Alkenes are used in a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications.
- Alkenes are used as starting materials for the production of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Alkenes are used as solvents.
- Alkenes are used as fuels.
- Alkenes are used in the production of synthetic rubber.
- Alkenes are used in the production of pharmaceuticals.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of systematic alkene nomenclature?
Systematic alkene nomenclature ensures consistency and clarity in naming these compounds, allowing for unambiguous identification and communication among scientists.
How does the IUPAC system assign names to alkenes?
The IUPAC system considers the parent chain, double bond location, and substituents to assign systematic names to alkenes.
What are the key features that distinguish alkenes from other hydrocarbons?
Alkenes are characterized by the presence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds, which imparts unique chemical and physical properties.