The eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer” in depth answers pdf takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a tightly regulated process that ensures the accurate duplication and segregation of chromosomes. Disruptions to the cell cycle can lead to cancer, a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division.
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
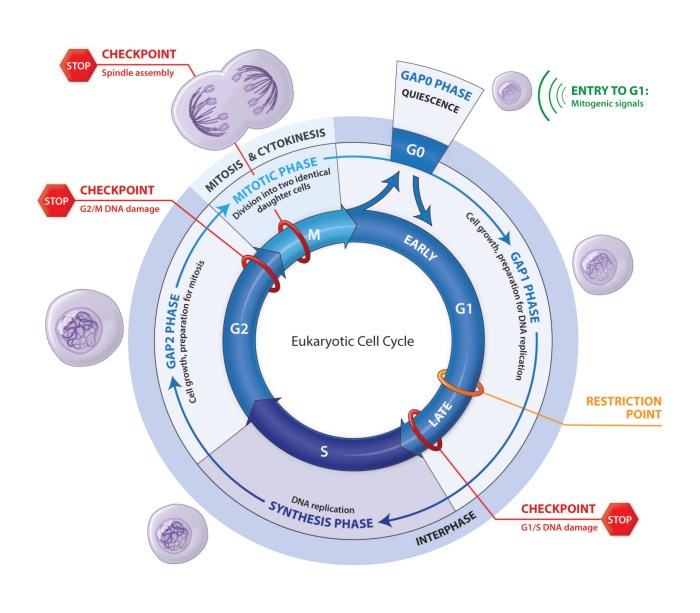
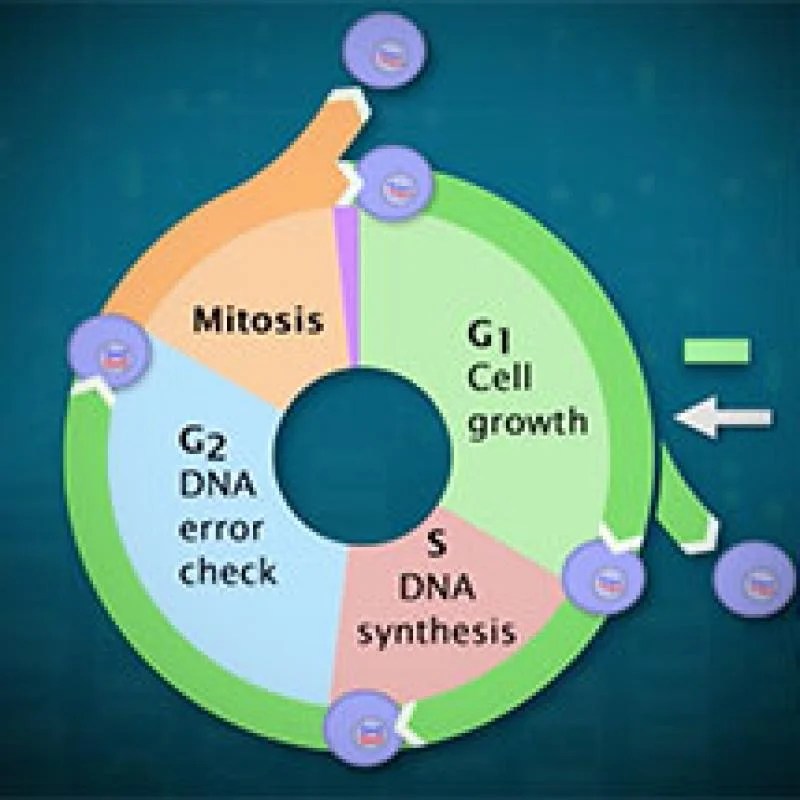
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a series of events that occur in a cell leading to its division and duplication. It consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and M. During the G1 phase, the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
In the S phase, DNA replication occurs, resulting in two identical copies of each chromosome. The G2 phase is a period of growth and preparation for mitosis. Finally, during the M phase, mitosis occurs, resulting in the division of the cell into two daughter cells.
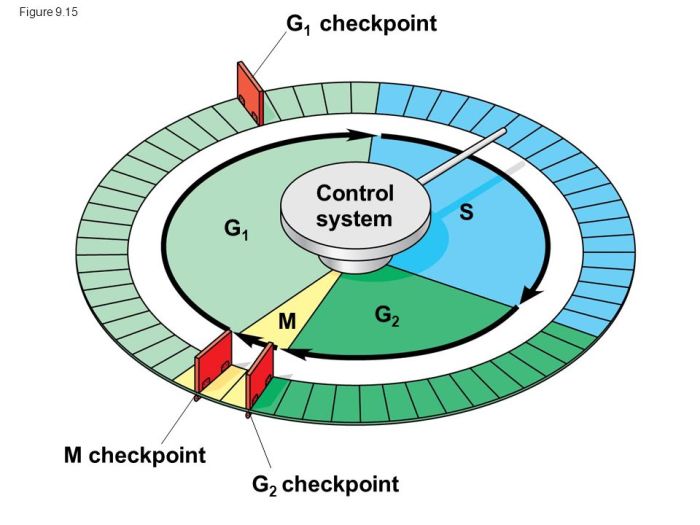
Checkpoints in the Cell Cycle
Checkpoints are control mechanisms that ensure the cell cycle proceeds correctly. There are three main checkpoints: the G1/S checkpoint, the S/G2 checkpoint, and the G2/M checkpoint. These checkpoints monitor the cell’s progress through the cell cycle and can halt the cycle if conditions are not favorable for cell division.
Factors Influencing the Cell Cycle
Several factors can influence the cell cycle, including growth factors, hormones, and environmental conditions. Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell growth and division. Hormones are chemical messengers that can regulate the cell cycle. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and pH, can also affect the cell cycle.
Cancer and the Cell Cycle: The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle And Cancer” In Depth Answers Pdf
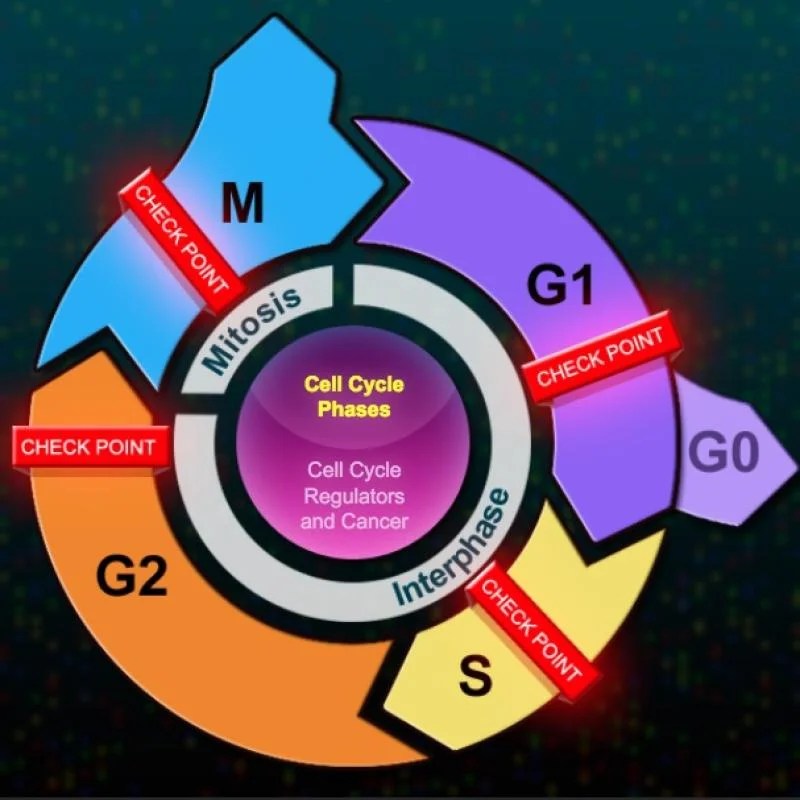
Cancer cells are characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division. They often evade cell cycle checkpoints, allowing them to divide uncontrollably. This uncontrolled cell division can lead to the formation of tumors.
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes
Oncogenes are genes that promote cell growth and division. Mutations in oncogenes can lead to cancer. Tumor suppressor genes are genes that inhibit cell growth and division. Mutations in tumor suppressor genes can also lead to cancer.
Cancer Treatments Targeting the Cell Cycle
Several cancer treatments target the cell cycle. These treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells by damaging their DNA or disrupting their cell cycle. Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells without harming healthy cells.
Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle and Cancer
Various methods are used to study the cell cycle and cancer. These methods include microscopy, flow cytometry, and molecular biology techniques.
Microscopy
Microscopy is a technique used to visualize cells and their components. It can be used to study the cell cycle by observing the changes in cell morphology that occur during the different phases.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique used to measure the size, shape, and DNA content of cells. It can be used to study the cell cycle by analyzing the distribution of cells in the different phases.
Molecular Biology Techniques
Molecular biology techniques, such as PCR and DNA sequencing, can be used to study the cell cycle by analyzing the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation.
Clinical Applications of Cell Cycle Research
Cell cycle research has led to several clinical applications, including the development of cell cycle markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis, and the development of cell cycle-targeted therapies for cancer.
Cell Cycle Markers
Cell cycle markers are proteins that are expressed during specific phases of the cell cycle. These markers can be used to identify cells that are actively dividing, which can be helpful in diagnosing cancer.
Cell Cycle-Targeted Therapies, The eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer” in depth answers pdf
Cell cycle-targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target cancer cells by disrupting their cell cycle. These therapies include drugs that inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are enzymes that regulate the cell cycle.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key stages of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
The key stages of the eukaryotic cell cycle are: G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase (mitosis).
How do cancer cells evade cell cycle checkpoints?
Cancer cells can evade cell cycle checkpoints by mutating the genes that encode checkpoint proteins or by overexpressing proteins that inhibit checkpoint function.
What are the different types of cancer treatments that target the cell cycle?
The different types of cancer treatments that target the cell cycle include: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.